|
Key takeaways:
|
|---|
What are biometric payments?
Biometric payments are transactions that use human physical attributes, such as fingerprint, palm, facial features, iris, and voice, to authenticate and confirm a customer’s intent to purchase. Like a person’s signature, these biometric characteristics are unique for each individual and are hard to replicate. This makes biometric payment one of the most secure contactless payment methods today.
Modern biometric payment began in the early 2000s when John Rogers founded the Pay By Touch service, which allows customers to pay by scanning their fingerprints. Apple followed soon after, launching Touch ID technology in 2013 as a key feature of the iPhone 5S. Today, fingerprint scanners are in almost every smartphone, tablet, and laptop, used to secure personal information and confirm mobile payments.
Who should use biometric payments?
Customers can set up fingerprint authentication on their smartphones and use it to authenticate their payments. So any ecommerce or brick-and-mortar store regardless of business type can accept biometric payments if it already supports digital wallet payments such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, PayPal, and the like.
A merchant-based biometric payment setup, such as those often used in government, private offices, and even schools, requires considerable hardware and software investment. In general, you should invest in a biometric scanner if your business:
- Serves customers in person: Customers will have to be physically present to register and scan their fingerprint or palm to confirm their payment. A great example would be retailers with self-service kiosks like grocery stores or fast food restaurants.
- Caters to a younger demographic: Younger costumes are more open to setting and signing up for new payment methods
- Enables better customer experience: Adding biometric payments to a POS system that’s already integrated with CRM and loyalty management systems can significantly boost customer experience, from the first purchase to repeat transactions.
- Offers subscriptions: Biometric registration integrated within the sign-up process gives customers an increased sense of security, which can build loyalty and attract new customers. Healthcare services are a good example.
How do biometric payments work?
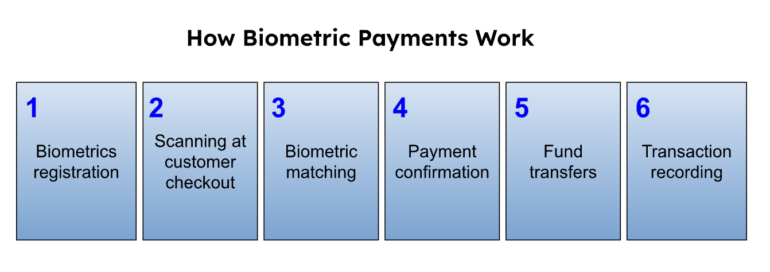
- The customer registers their biometrics information with a store. This is then added to the customer’s profile and encrypted.
- When the customer next shops in the store, the merchant’s system will prompt for biometric authentication to complete the purchase via the biometric scanner.
- The system searches its stored biometric data based on the customer name and matches it against the features captured by the biometric scanner.
- If the biometric data matches, the transaction is confirmed and a receipt is generated. Otherwise, the system alerts the cashier and prompts for a rescan.
- The customer’s chosen payment method is debited with the purchase amount while the merchant receives the proceeds of the transaction less the processing fees.
- The customer’s source of funds and the merchant’s POS and payment processor records the transaction.
For online businesses, biometric payment authentication is connected to mobile wallet apps. The transaction process follows any other NFC payment method used on online payment gateways with the added biometric security prompted by the customer’s smartphone.
SEE: 5 Online Payment Methods for Small Businesses To Try
What is a biometric scanner?
The biometric scanner is the technology at the core of biometric payments. It is a combination of:
- Hardware that captures the biometric attribute via a near-infrared (NIR) sensor, smart camera, or microphone, and
- Software that stores the biometric data.
The scanner also replaces the role of a password or PIN so that only individuals whose biometrics are stored in the system can gain access to the asset the security is protecting. This includes allowing a person to use a source of funds to complete a transaction.
Types of biometric authentication
There are several means of processing biometric authentication:
- Fingerprint scanning: The scanner records multiple point-to-point measurements of an individual’s fingerprint (usually the index or thumb).
- Palm vein scanning: The scanner captures the vein patterns from the individual’s palm. ‘
- Facial mapping: The scanner captures “facial landmarks” and measures features such as the distance between points, slopes, ridges, and angles of the face.
- Iris scanning: The scanner identifies and records the unique characteristics of an individual’s iris.
- Voice recognition: Records an individual’s voice sample and identifies accents, inflection points, and tone.
In principle, biometric authentication is applied to provide security and monitor events by confirming identity. You will likely be more familiar with it being used to access a secure location, register identity with a bank, school, or government body, unlock phones or laptops, and confirm attendance than as a means to protect your source of funds during payments.
That said, consumers are becoming more open to biometrics payments thanks to smartphones.
What are the different biometric payment methods available today?
The most widely adopted biometric payment methods available today are fingerprint and palm scanning. And, though still rare, there are also recent developments in the use of iris scans, voice recognition, and facial mapping to authenticate payments.
Biometric payments examples
Why are biometric payments so popular today?
As consumers demand for faster and more convenient means of making payments without sacrificing security, fintechs continue to push the boundaries of contactless payments with biometrics. The use of biometric attributes to authenticate transactions improves security while the built-in automation expedites the checkout process, giving an overall better customer experience.
Smartphone providers also helped considerably in preparing consumers by introducing fingerprint scanning.
SEE: Best Mobile Credit Card Processing Solutions
Advantages of biometric payments
Both merchants and customers can benefit from biometric payments:
- Faster checkout: A biometric payment system provides customers with a faster checkout process. Instead of tapping or hovering a card or smart device near an NFC card reader, all the customer needs to do is get their preferred biometric feature scanned via a smart camera or infrared sensor.
- Competitive advantage: As the younger demographic grows into adults, merchants equipped with advanced payment methods, such as biometric payments, will have a better chance of attracting new and retaining current customers.
- Increased customer loyalty: Merchants that can offer the best customer checkout experience will find it easier to build customer loyalty. Customers will know that their financial data is better secured with biometric authentication and, in turn, build the business reputation.
- Better customer relationship management: Customers who elect to enroll in biometric payment build their customer profile at the same time. This allows merchants to personalize their loyalty rewards by tracking purchase history.
- Enhanced payment security and fraud prevention: Transactions are more secure with biometric authentication in place. The unique physical attributes are more difficult to steal or replicate, thereby being more effective to prevent fraud. This also means less chargeback claims and better chargeback ratio.
Disadvantages of biometric payments
As with any advanced technology, biometric payments can still bring some disadvantages:
- Significant investment: Merchants looking to install a biometric payment system will need to invest in hardware and software. Businesses are at the mercy of third-party providers that dictate the cost of the investment.
- Physical set up requirements: To launch a biometric payment system, merchants will need to physically set up hardware and software, which will require some downtime to integrate.
- Customer acceptance: Older customers might be less trusting of new technology. Younger customers will require some convincing. Merchants will need to train their sales representatives to, first, convince the customer to pause from their busy day to enroll their biometrics, and second, learn how to use the system.
- Performance limitations: Even with sophisticated technology, the accuracy of biometric payments also depend on external factors, such as a clean or damaged sensor, system bugs, and the like, which can lead to flaws in stored data or inability to recognize a legitimate user.
- Regulatory compliance: Data privacy is a serious concern; biometric data is equally sensitive as a customer’s financial and personal information. Using a third-party provider for a biometric payment system creates an additional channel that hackers can exploit for vulnerability.
Please note: In general, biometric data is recognized as sensitive personal information, which, when collected (and stored) along with the customer’s financial information upon biometric enrollment, is thoroughly protected under PCI DSS compliance.
The future of biometric payments
Adoption
According to the Business Research Company, the biometrics payment market was valued at $42.86 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $46.61 billion by the end of 2025. While current available infrastructure still limits the adoption of biometric payments in mainstream retail, the technology will certainly continue to evolve into a more accessible and cost-effective solution.
- Since 2022, Mastercard has been aggressively partnering with fintechs and payment hardware providers to launch a wide range of biometric payment methods around the globe.
- Amazon launched its “Amazon One” biometric payment program that allows its enrolled customers to pay for their groceries at participating Whole Foods stores via palm vein scanning.
- CLEAR developed a biometric payment app for stadiums to sell tickets with an added age verification feature. The same technology is used for identity verification in airports (TSA PreCheckⓇ).
Technology
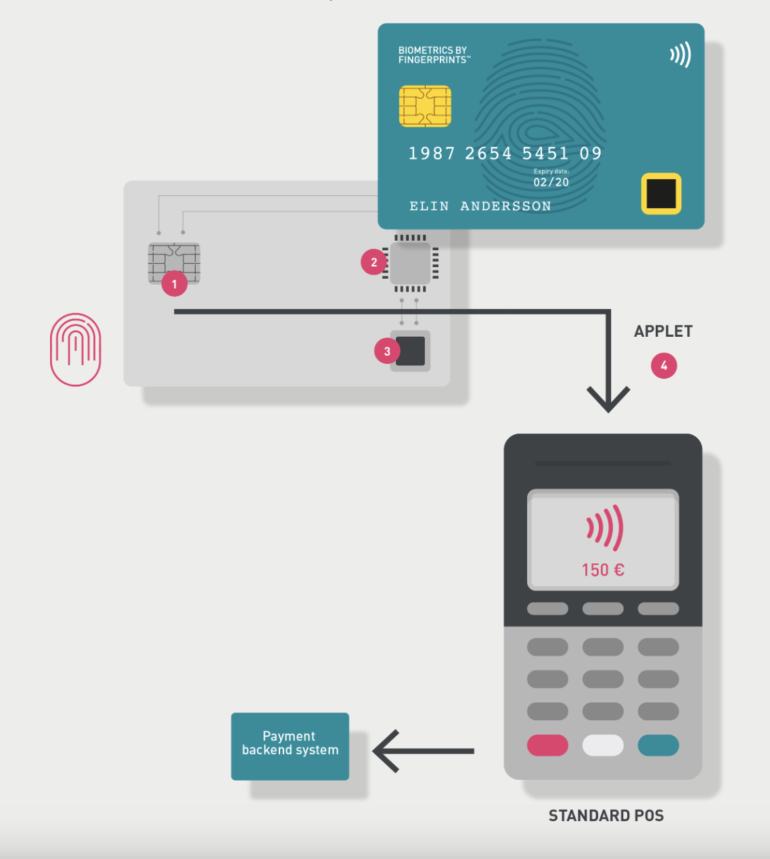
- Fingerprint payment cards: One of the latest developments in biometric technology is fingerprint recognition-enabled payment cards. The card has a built-in fingerprint sensor and is only activated when it’s near a POS terminal or card reader.
- Behavioral biometrics: In Australia, a company called BioCatch developed behavioral biometrics to detect potential unauthorized credit card use online. The system analyzes behaviors, such as inactivity, typing cadence, and OTP dictation, to detect fraudulent transactions.
- DNA ID: The “Rapid DNA” technology now makes it possible to create a small-bit DNA profile enough to embed a DNA ID in a portable storage device like a card. A DNA ID card is both unique and tamper-proof which developers see as a potential alternative to current biometric payment methods. However, most consumers associate DNA collection to criminal investigations, which hinders any chance of adoption for now.
Regulations and compliance
As adoption grows and biometric payments expand into cross border transactions, expect governments around the world to eventually develop a standardized regulation for biometric payments.
At the moment, there are no specific, standardized global regulations for biometric payments though country-specific rules do exist. For instance, Illinois was the first state to enact a biometric privacy law in 2008. The Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) established requirements for use and storage of biometric data.
California, on the other hand, includes biometrics as protected consumer data in its California Consumer Privacy Act. In Europe, biometric payments are covered by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2).
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is biometric payment safe?
Yes, unique biometric physical attributes are harder to steal compared to PIN codes and passwords. The storage protocols used to keep your biometric information follow similar strict compliance standards for storing financial data.
Which biometric type is the best?
In terms of accuracy, iris recognition is the most secure and hardest to copy. Fingerprints scanning is the fastest and least expensive to set up.
Who pays biometric fees?
Aside from card processing fees, there are no additional transaction-related costs charged to the customer or merchant. That said, setup costs of a biometric payment system is the merchant’s responsibility.